Duoflora – Lactobacillus Rhamnosus GG
Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG (Lactobacillus GG) is an Adult Human-Derived Probiotic strain that has garnered extensive attention for its profound health benefits. One of the key strains in Duoflora, this powerful strain has been the subject of numerous studies and is recognized for its efficacy in addressing a variety of health concerns. Let’s delve into the specific benefits of Lactobacillus GG and understand why it stands out in the realm of probiotics.
Harnessing the Power of Lactobacillus Rhamnosus GG

Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG is a human strain probiotic isolated from the intestines of healthy adults, ensuring it is a naturally occurring and safe probiotic strain. It is classified as Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS) by regulatory authorities, underlining its safety for consumption.
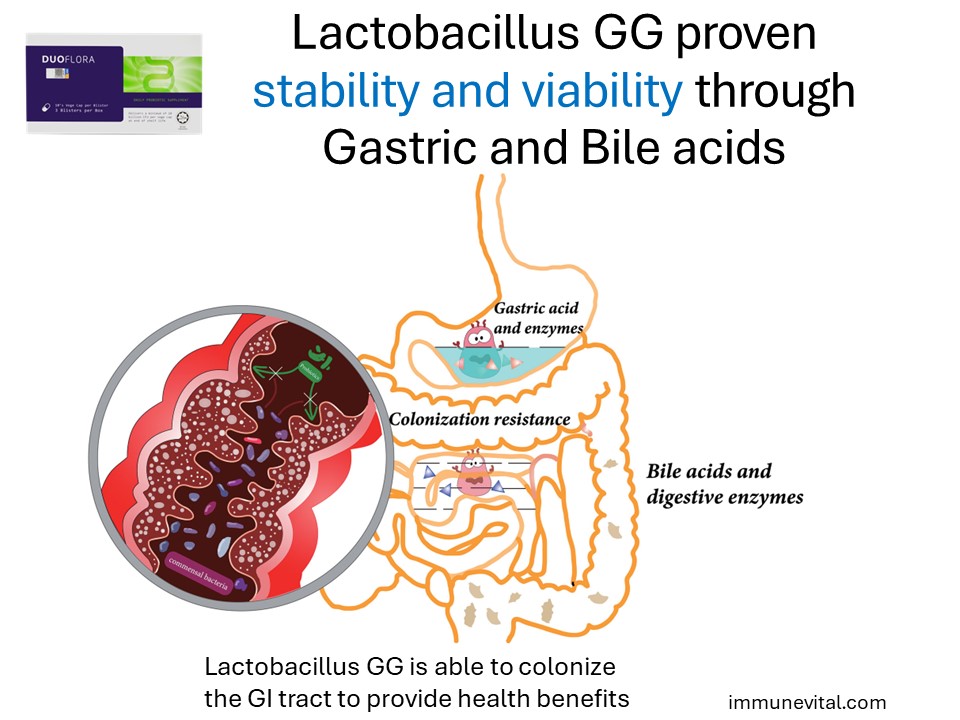
Stability and Viability
Lactobacillus GG has been shown to be stable and viable through gastric and bile acids to colonize the intestines and provide health benefits
Eczema Relief
Lactobacillus GG has shown significant promise in managing eczema, particularly in infants and young children. Research indicates that supplementation with Lactobacillus GG can help reduce the severity of eczema symptoms by modulating the immune response and decreasing skin inflammation. This makes it a valuable addition for those struggling with atopic dermatitis.
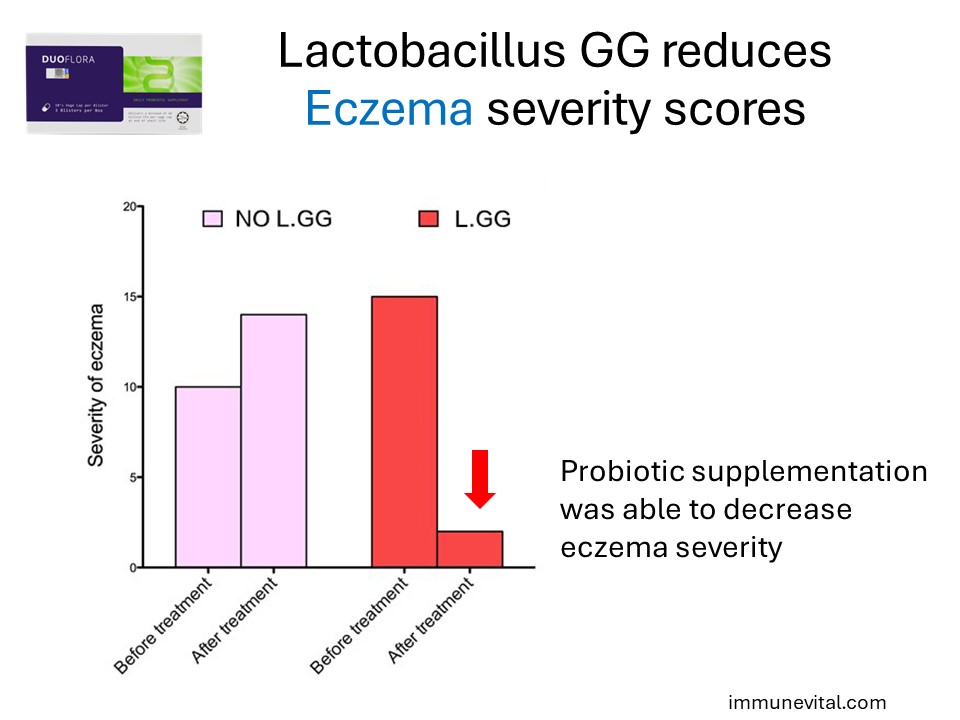
The study above involved a total of 27 infants, mean age 4.6 months, who manifested atopic eczema during exclusive breast-feeding. It demonstrated that supplementation with Lactobacillus GG can reduce eczema severity scores.
Prevention of Eczema
In addition to treating existing eczema, Lactobacillus GG has been shown to play a preventative role. Prenatal and postnatal supplementation with Lactobacillus GG can significantly reduce the risk of developing eczema in infants, providing long-term benefits from an early age.
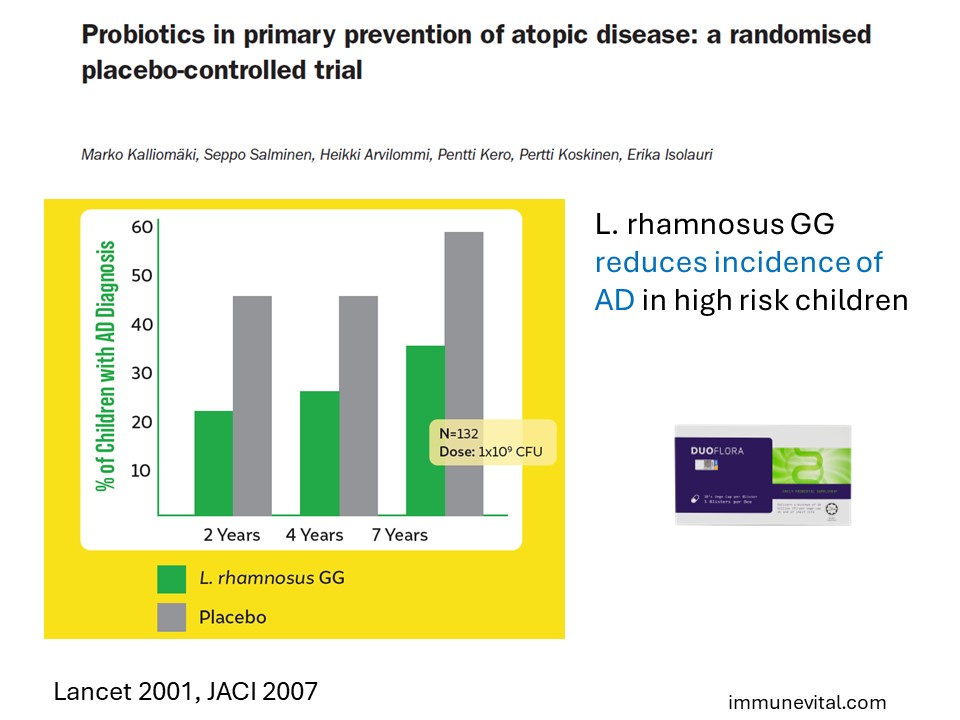
The study above was an important landmark clinical trial that was conducted in Finland. It was a double-blind, randomized placebo-controlled trial where Lactobacillus GG were given prenatally to mothers and postnatally for 6 months to their infants. The mothers had at least one first-degree relative (or partner) with atopic eczema, allergic rhinitis, or asthma.
Pregnant mothers consumed Lactobacillus GG before delivery. After delivery, those mothers who went on to breastfeed their babies continued to consume this GG probiotic themselves for 6 months. For those babies who could not receive breast milk, the probiotic was fed to the babies directly for the same period of time. It was found that in the babies who were exposed to Lactobacillus GG probiotic strain either directly or indirectly through breastfeeding, development of allergic eczema was reduced by 50% as compared to those babies who were not exposed.
Lactobacillus GG was effective in PREVENTING ECZEMA in children at high risk with results seen from 2 years of age up to 7 years old. This finding provided evidence that very early exposure to GG probiotic reduced the risk of a baby becoming allergic and that the protection was long term.
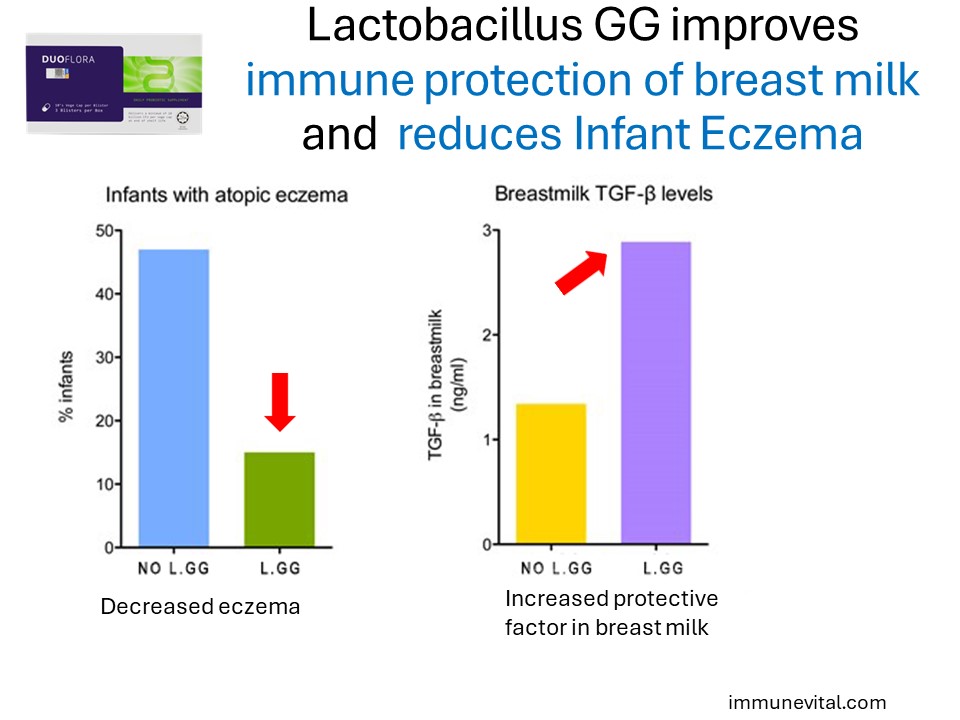
In this double-blinded, placebo-controlled study of 62 mother-infant pairs, it is shown that administering Lactobacillus GG to the pregnant and lactating mother increased the immune protective potential of breast milk, as assessed by the amount of anti-inflammatory Transforming Growth Factor β2. This immune factor suppressed allergic inflammation resulting in their breastfed babies having around 68% less risk of developing atopic eczema. The risk of developing atopic eczema during the first 2 years of life in infants whose mothers received probiotics vs placebo was 15% and 47% respectively.
Food Allergy Management
Food allergies can significantly impact quality of life. Lactobacillus GG has been found to help infants that have developed food allergies to develop tolerance and outgrow their food allergy.
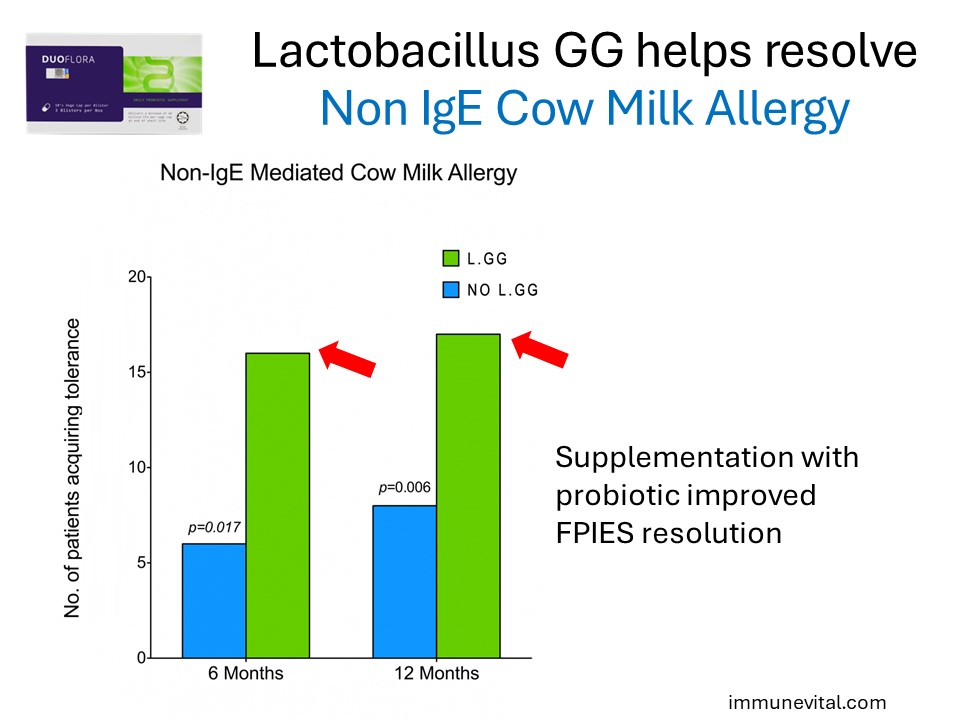
The study above looked into infants that develop Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome (FPIES), a severe form of non-IgE mediated food allergy to cow milk protein. Supplementation of extensively hydrolyzed cow milk formula with Lactobacillus GG accelerated the development of tolerance in infants to cow milk protein.
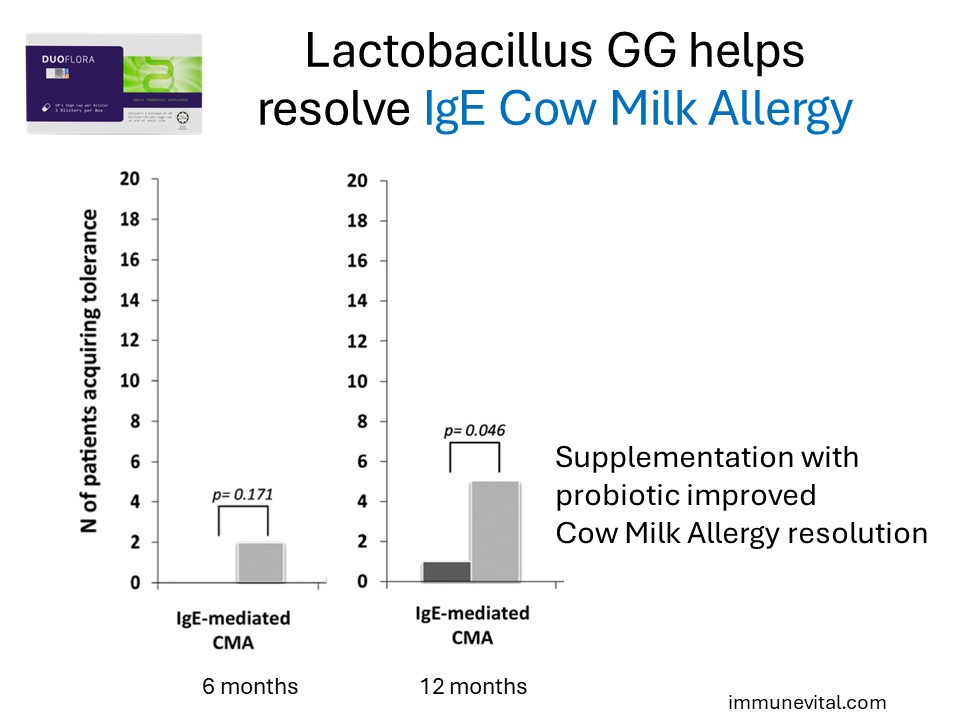
The same study also found that Lactobacillus GG helped children with IgE mediated cow milk allergy develop resolution of their allergy.
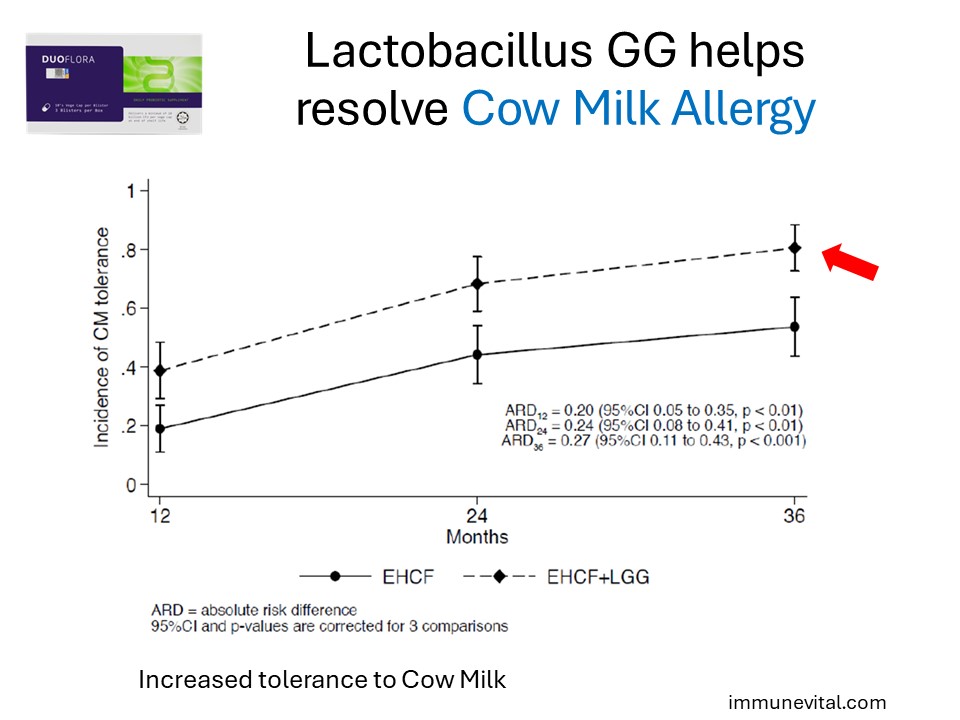
In the study above, a total of 220 children with a median age of 5.0 months were randomized; 110 children were placed in the Extensively Hydrolyzed Cow Milk Formula group, and another 110 children were placed in the same Extensive Hydrolyzed Cow Milk Formula with Lactobacillus GG. The probiotic group demonstrated increased resolution and tolerance to cow milk
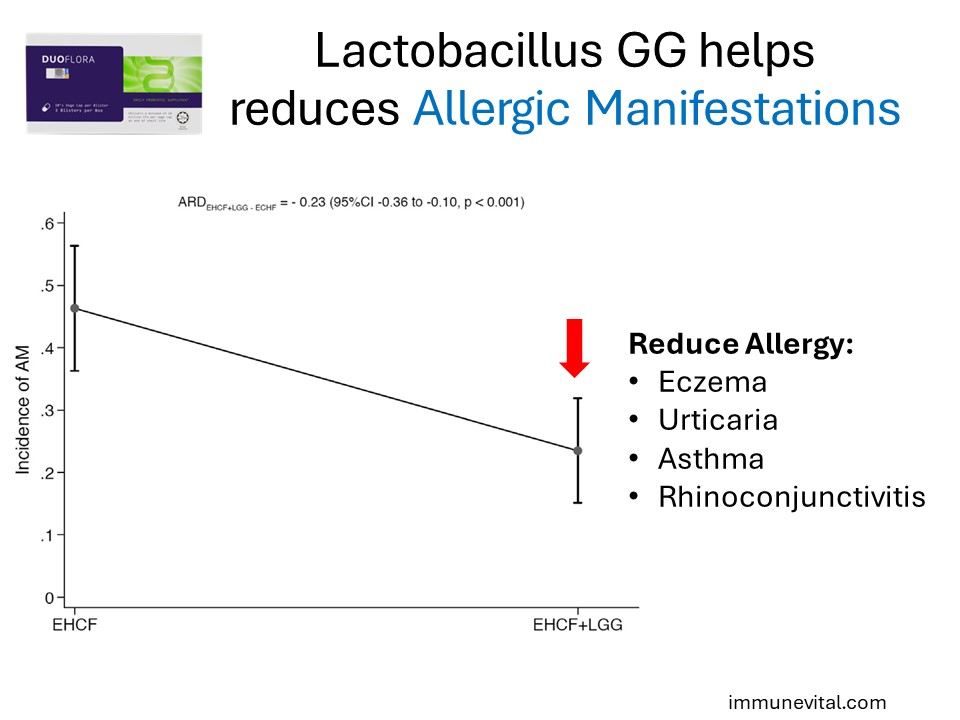
In the same study, the probiotic group also demonstrated reduced incidence of allergic manifestations.
Helps Allergic Rhinitis and Asthma
For individuals suffering from allergic rhinitis and asthma, Lactobacillus GG offers substantial benefits. Studies have shown that Lactobacillus GG can help alleviate the symptoms of allergic rhinitis and reduce asthma-related wheezing by modulating immune responses and reducing inflammation in the airways.
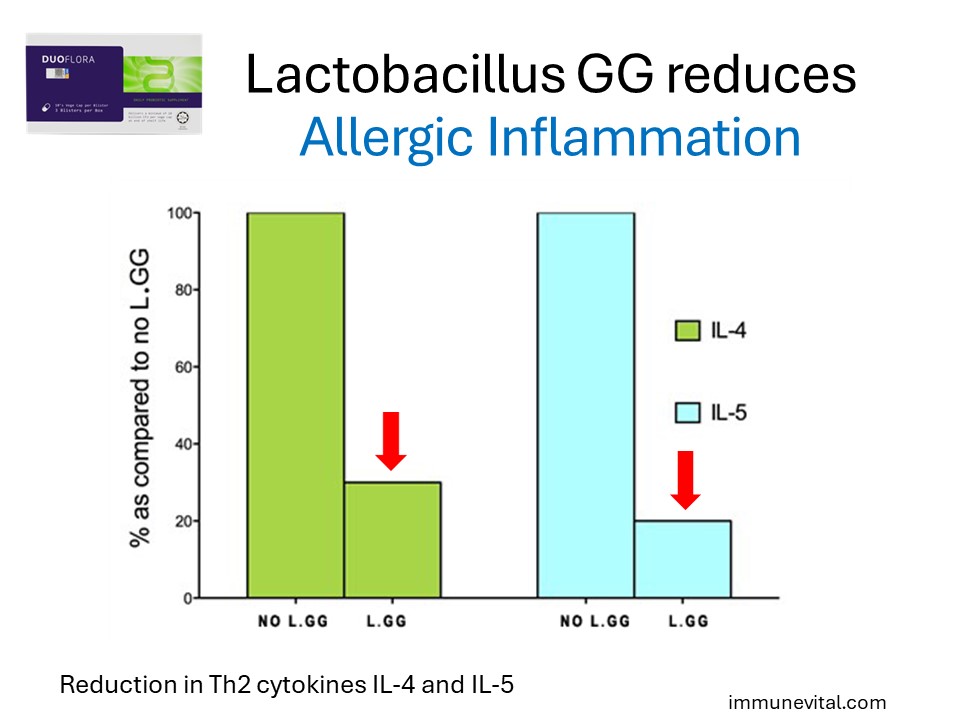
Probiotics or placebo was administered to 40 subjects with a clinical history of Japanese Cedar Pollen allergy for 10 weeks. The study showed a drop in production of allergic immune factors (IL-4 and IL-5) in allergic patients that were taking Lactobacillus GG.
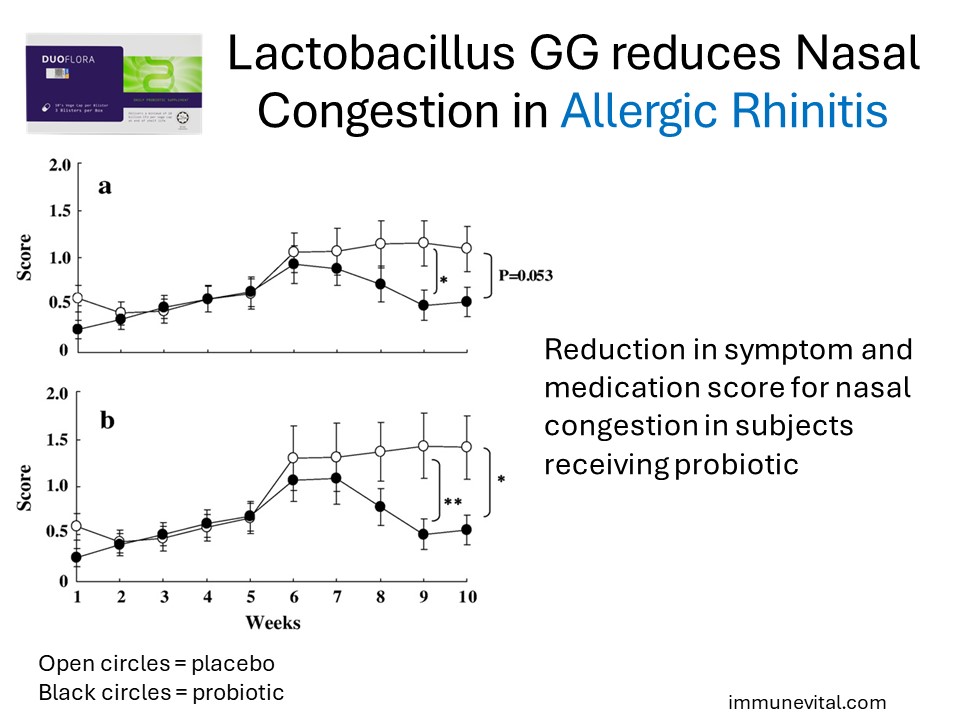
The study also showed that Lactobacillus GG significantly decreased the mean symptom score for nasal blockage after 9 weeks (P<0.05) and mean symptom-medication scores after 9 and 10 weeks when compared with the placebo group. Allergic rhinitis patients taking Lactobacillus GG will have less symptoms and decreased medication use.
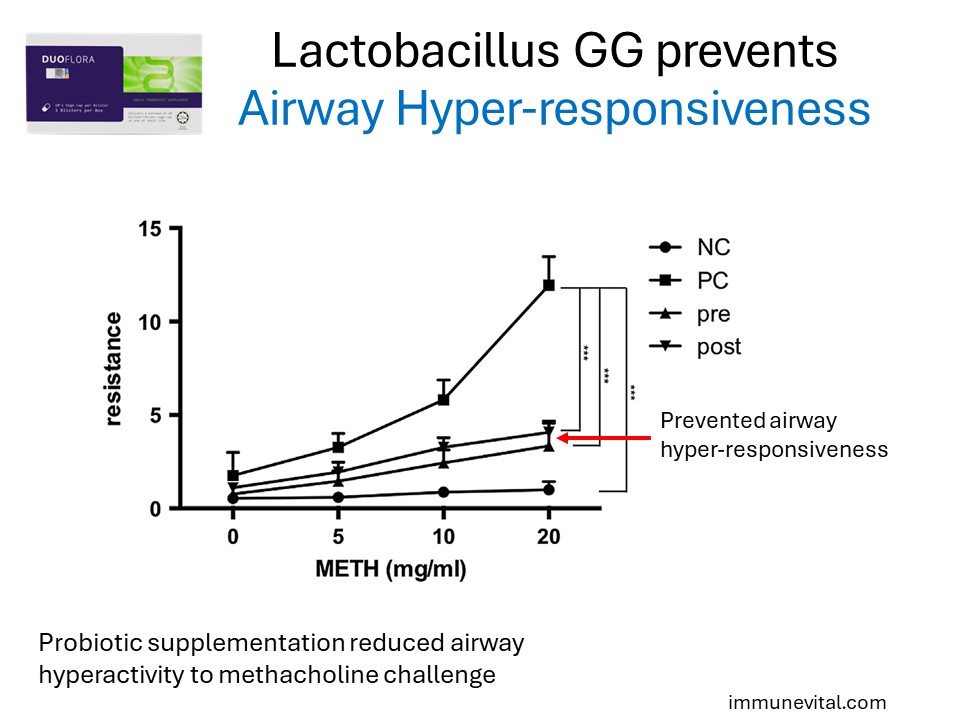
Lactobacillus GG also demonstrated the ability to prevent reactive airways in asthma by reducing sensitivity to methacholine.
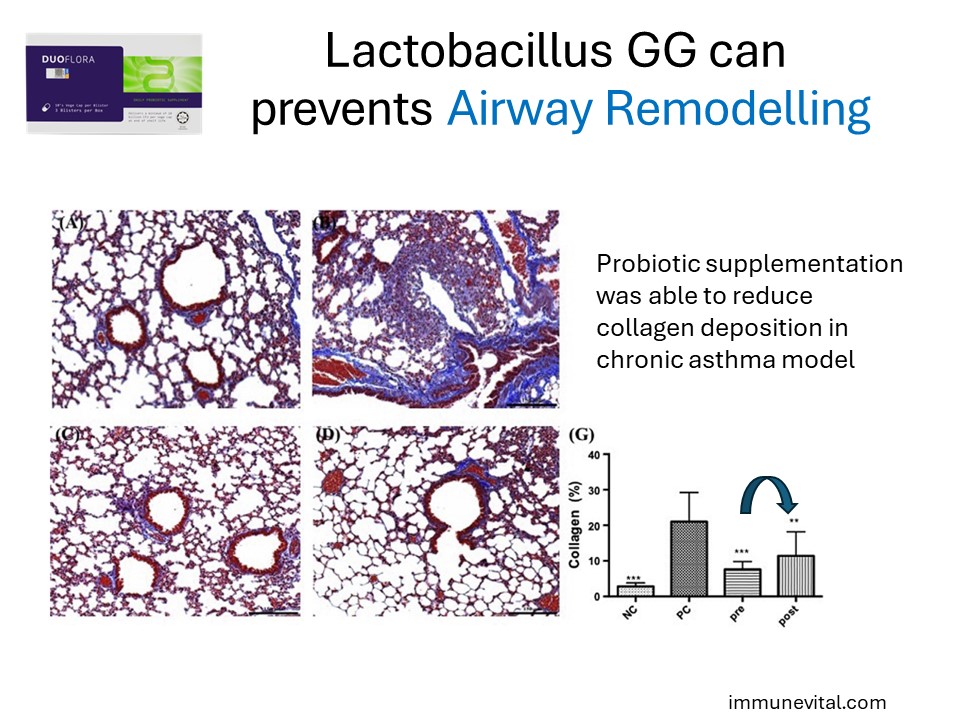
Lactobacillus GG supplementation was able to reduce collagen deposition in chronic asthma indicating the ability to prevent lung remodeling in asthma. This is important as remodeling can cause irreversible lung obstruction that does not respond to medications. This suggests that chronic asthmatic sufferers may benefit from Lactobacillus GG which can reduce lung reactivity and prevent remodeling.
Reduction in Infectious Diarrhea
Lactobacillus GG is well-documented for its ability to reduce the incidence and duration of diarrhea. Whether caused by infections, antibiotic use, or other factors, Lactobacillus GG helps restore gut balance and improve intestinal health, making it a crucial probiotic for managing diarrheal diseases.
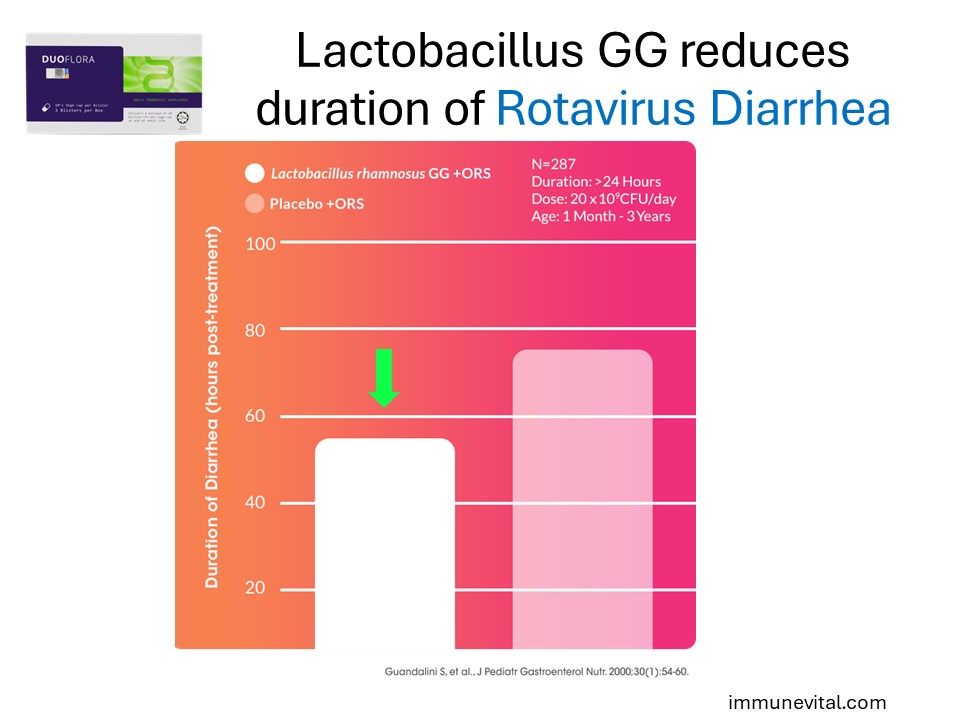
Clinical studies indicate Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG supplementation can reduce the duration of acute infectious rotavirus diarrhea, a common and serious infection in children.
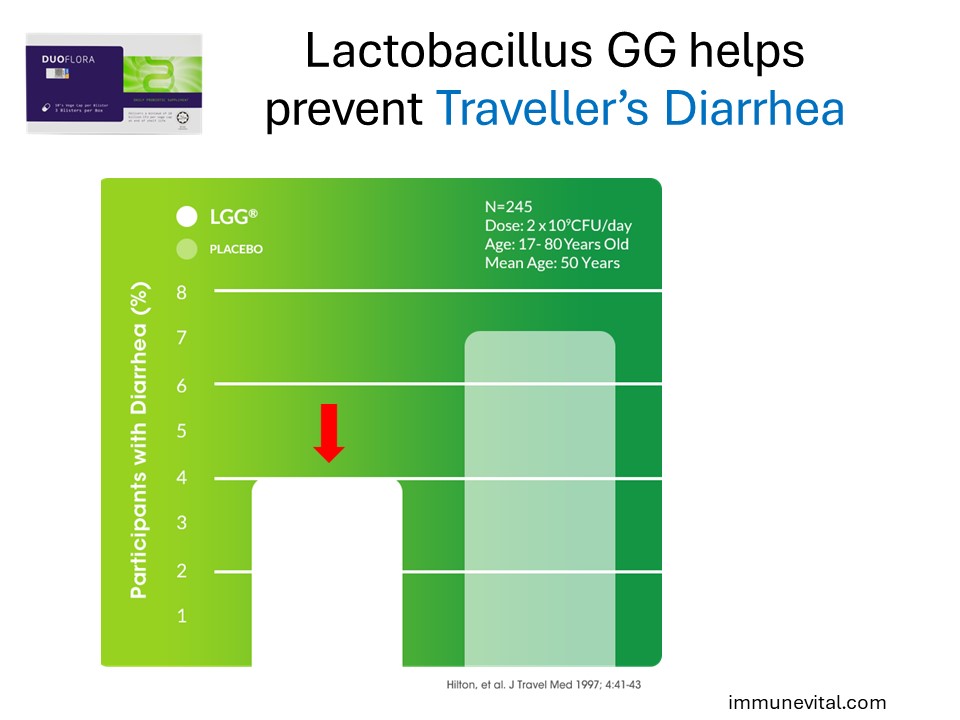
Travelers taking Lactobacillus GG were half as likely to experience diarrhea as compared to those in the placebo arm. The authors noted that for patients with a prior history of traveler’s diarrhea, the benefit of Lactobacillus GG administration was even greater.
A Solution for Antibiotic Associated Diarrhea
Antibiotic-associated diarrhea (AAD) is a common side effect of antibiotic use, affecting both children and adults. Antibiotics disrupt the natural balance of the gut microbiota, leading to a decrease in beneficial bacteria. This imbalance can result in diarrhea, characterized by frequent, loose, or watery stools. Lactobacillus GG is a well-studied probiotic strain known for its resilience and ability to colonize the gut. It has been extensively researched for its benefits in AAD.
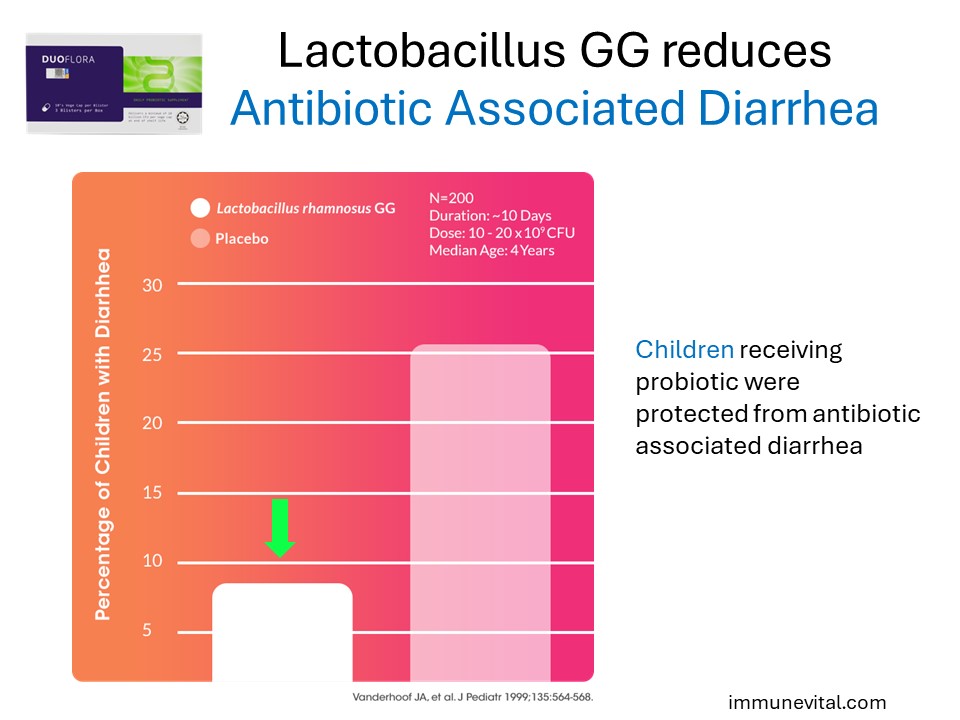
Children taking Lactobacillus GG with their antibiotics were significantly less likely to suffer from antibiotic- associated side effects like diarrhea.
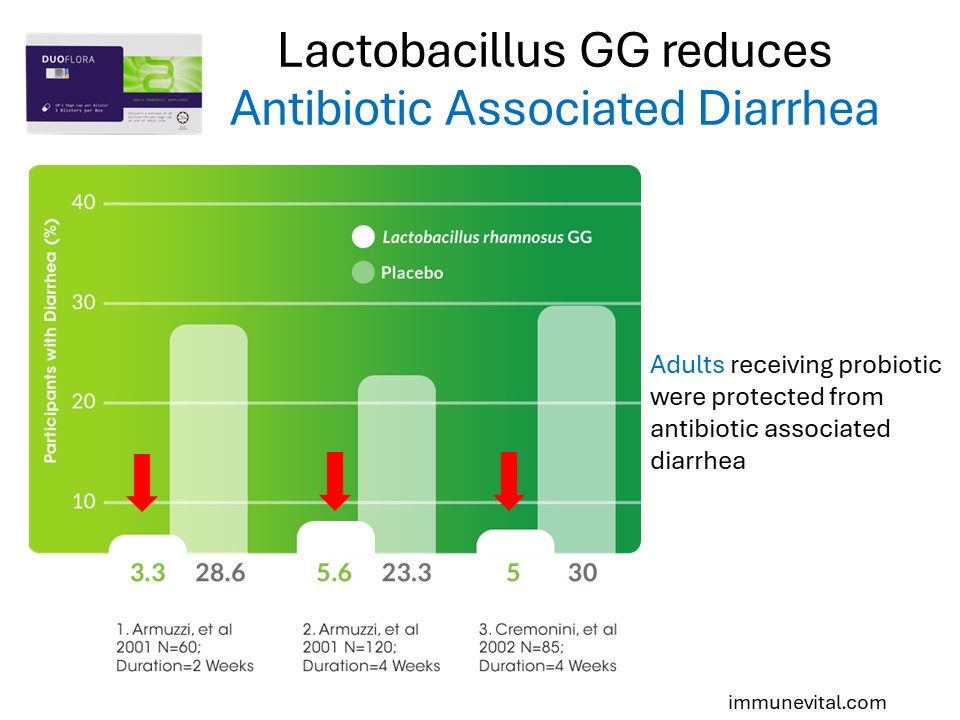
In the three studies above where triple therapy was used to eradicate H pylori infection in the stomach, Lactobacillus GG improves antibiotic treatment tolerability by reducing several side effects associated with triple therapy antibiotic regimen.
Reduction in Infections in Daycare and Hospitals
The probiotic properties of Lactobacillus GG extend to reducing infections in high-risk environments like daycares and hospitals. Regular intake of Lactobacillus GG has been associated with a lower incidence of respiratory and gastrointestinal infections, contributing to overall better health in communal settings.
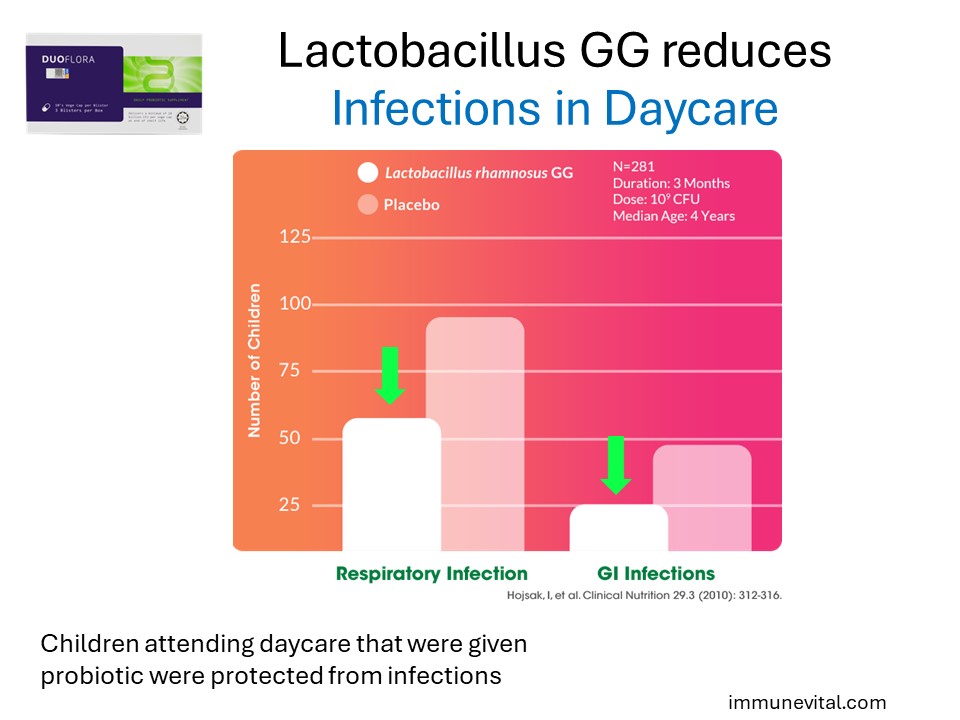
Children receiving Lactobacillus GG had a reduced risk of upper respiratory tract and gastrointestinal infections. It was found that those that were taking Lactobacillus GG and acquired respiratory infections had reduced severity with faster recovery.
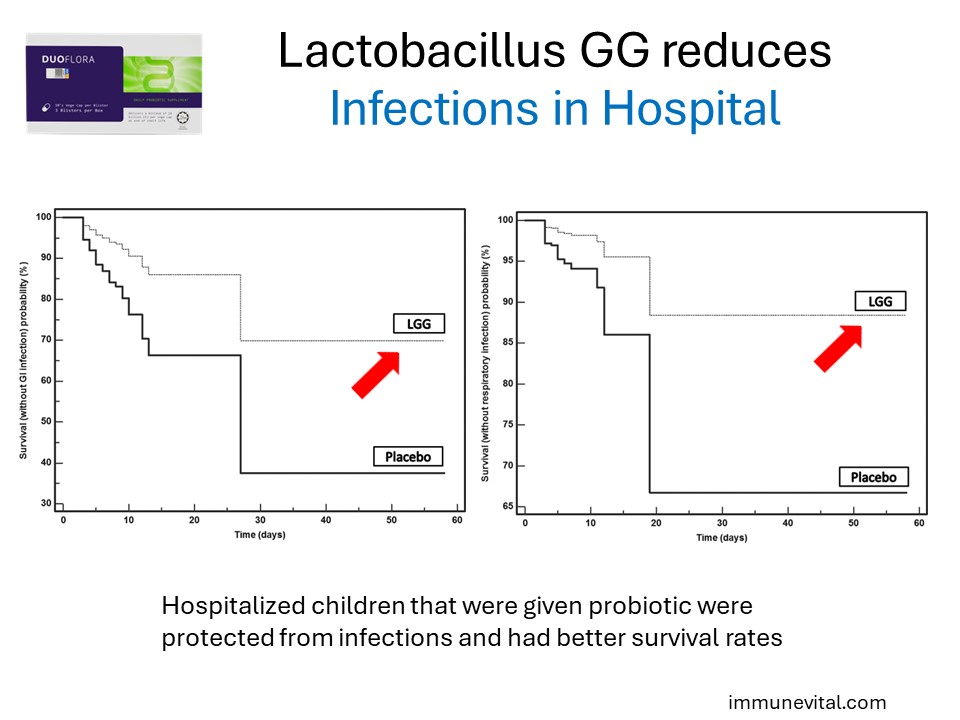
Hospitalized children are at greater risk for developing gastrointestinal and respiratory tract infections. A randomized, double blind, placebo-controlled trial above shows that Lactobacillus GG administration decreases the risk for nosocomial gastrointestinal and respiratory tract infections in hospitalized children.
Reduces Tooth Decay
Oral health is another area where Lactobacillus GG shines. Studies suggest that this probiotic can help reduce the occurrence of tooth decay by balancing the oral microbiota and inhibiting the growth of harmful bacteria that cause cavities.
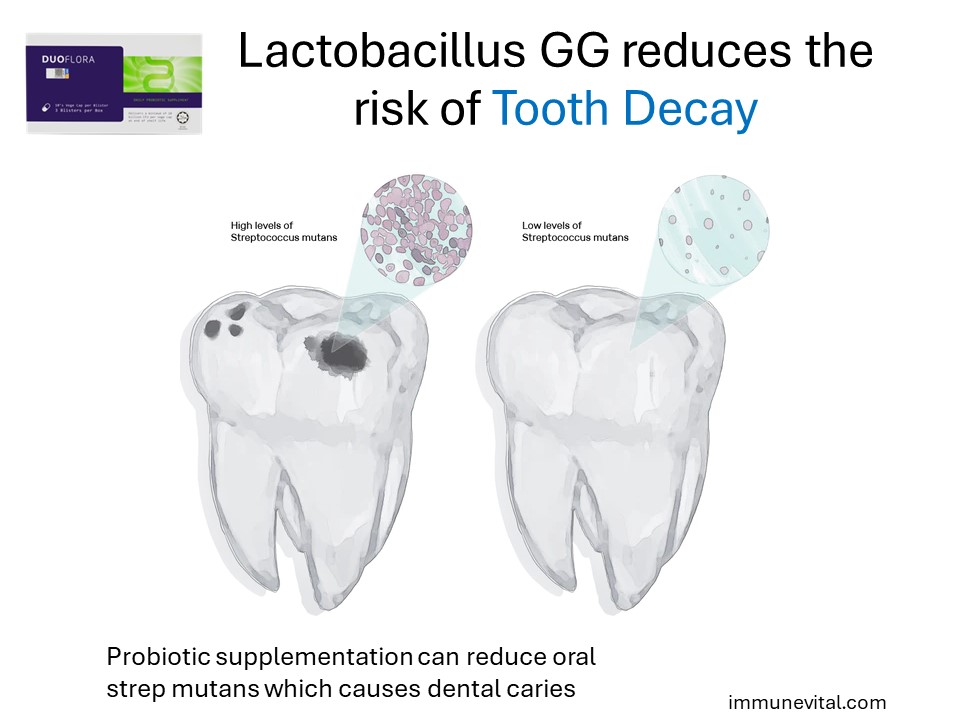
This randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled intervention study was designed to examine whether milk containing Lactobacillus GG has an effect on caries and the risk of caries in children when compared with normal milk. A total of 594 children, 1-6 years old, were studied for 7 months. The results showed less dental caries in the LGG group and lower mutans streptococcus counts at the end of the study. Lactobacillus GG was found to reduce the risk of caries significantly (OR = 0.56, p = 0.01; controlled for age and gender, OR = 0.51, p = 0.004).
To improve oral health, simple chew a capsule of Duoflora or empty the contents into the mouth and swallow normally. Do not eat and drink for 30 minutes to allow the probiotics to reduce problematic in the mouth to improve oral and dental health.
Reduces Irritable Bowel Syndrome Symptoms
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) can be a debilitating condition. Lactobacillus GG has been found to alleviate some of the common symptoms of IBS, including bloating, abdominal pain, and irregular bowel movements, thereby improving the quality of life for sufferers.
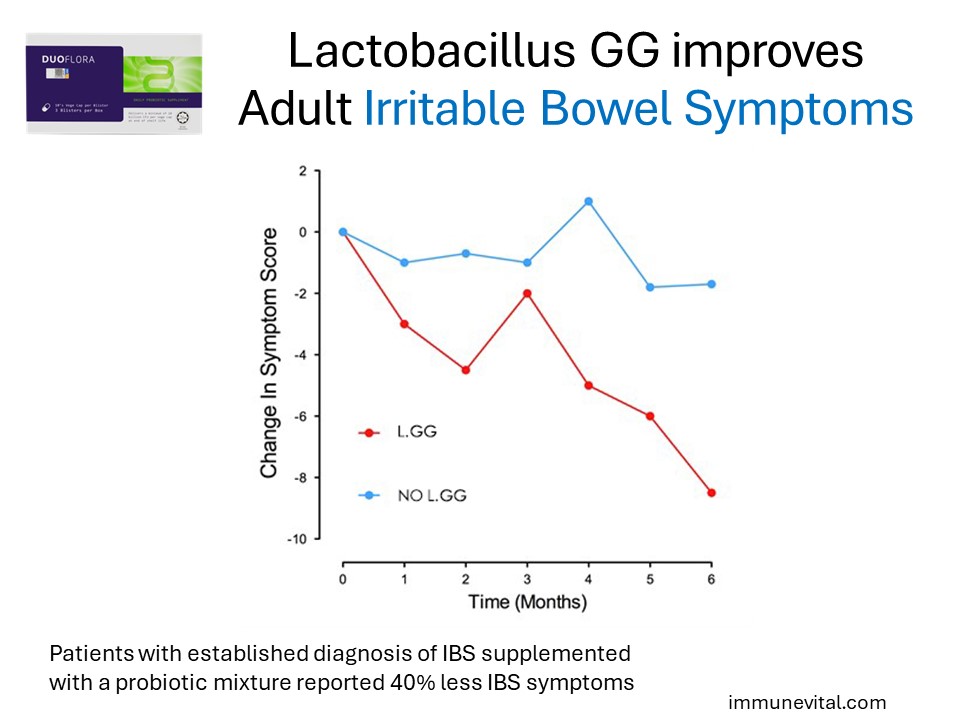
A total of 103 patients fulfilling the Rome I or II criteria took part in this 6-month, randomized, double blind placebo-controlled trial. The patients received a probiotic capsule or a placebo capsule daily. There was a median reduction of 42% in the symptom score of the probiotic group compared with 6% in the placebo group.
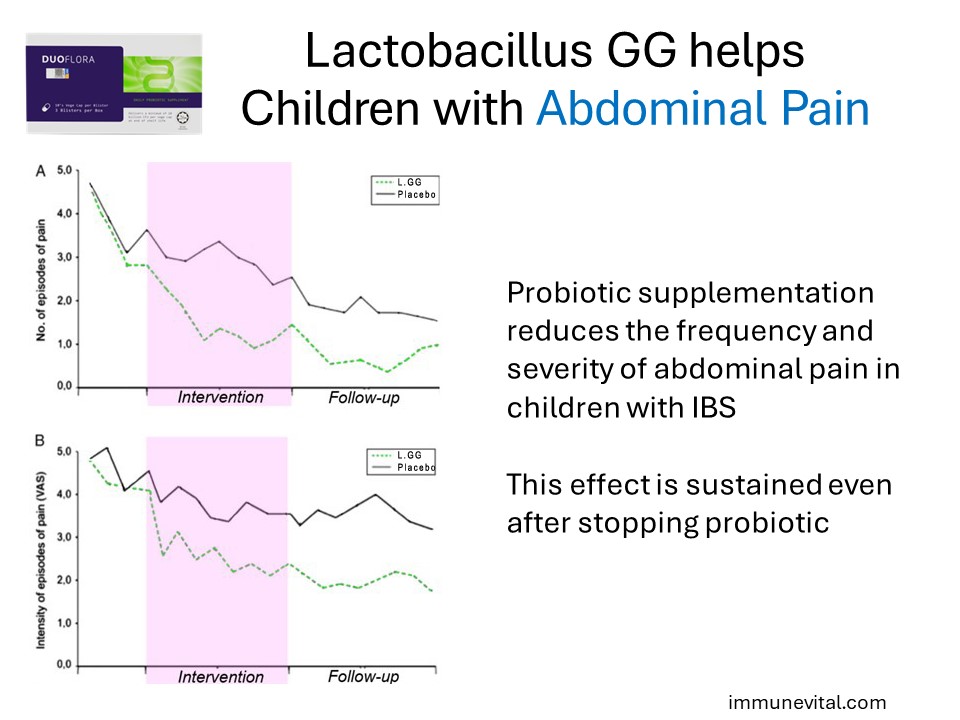
In the study above, a total of 141 children with irritable bowel syndrome or functional pain entered a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial and received Lactobacillus GG or placebo for 8 weeks and entered follow-up for 8 weeks. Compared with baseline, Lactobacillus GG, but not placebo, caused a significant reduction of both frequency (P < .01) and severity (P < .01) of abdominal pain. The improvement continued even after the probiotic was stopped.
Protects Against Fatty Liver
Emerging research points to the potential of Lactobacillus GG in protecting against alcohol and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). By modulating gut microbiota and reducing systemic inflammation, Lactobacillus GG may help prevent the accumulation of fat in the liver and support overall liver health.
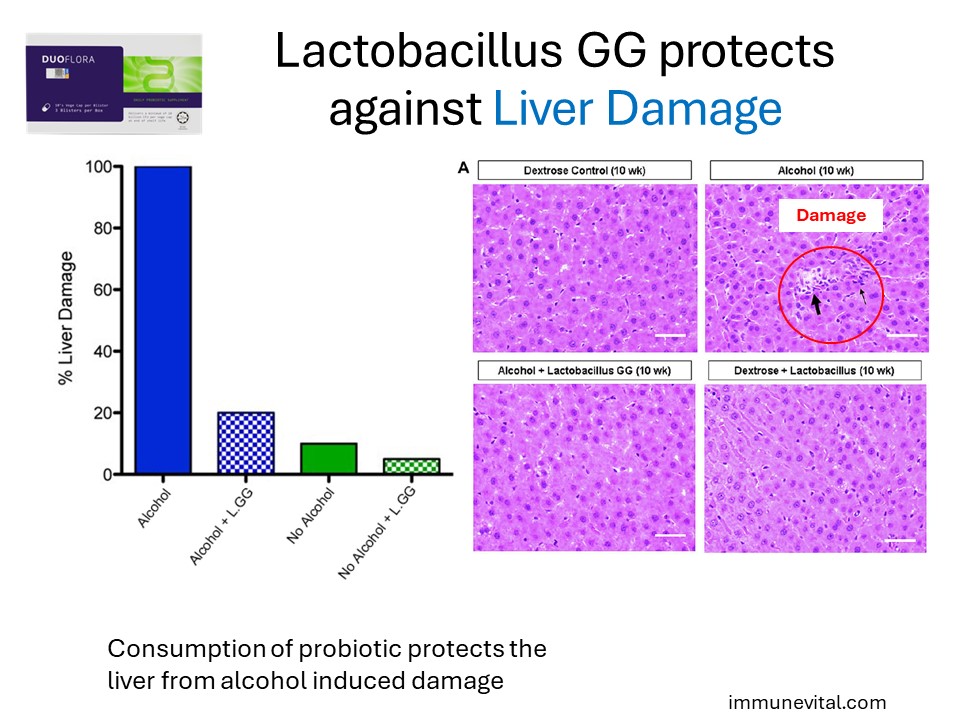
Lactobacillus GG was able to protect the liver from alcohol induced damage as evaluated through microscopic evaluation of liver tissues.
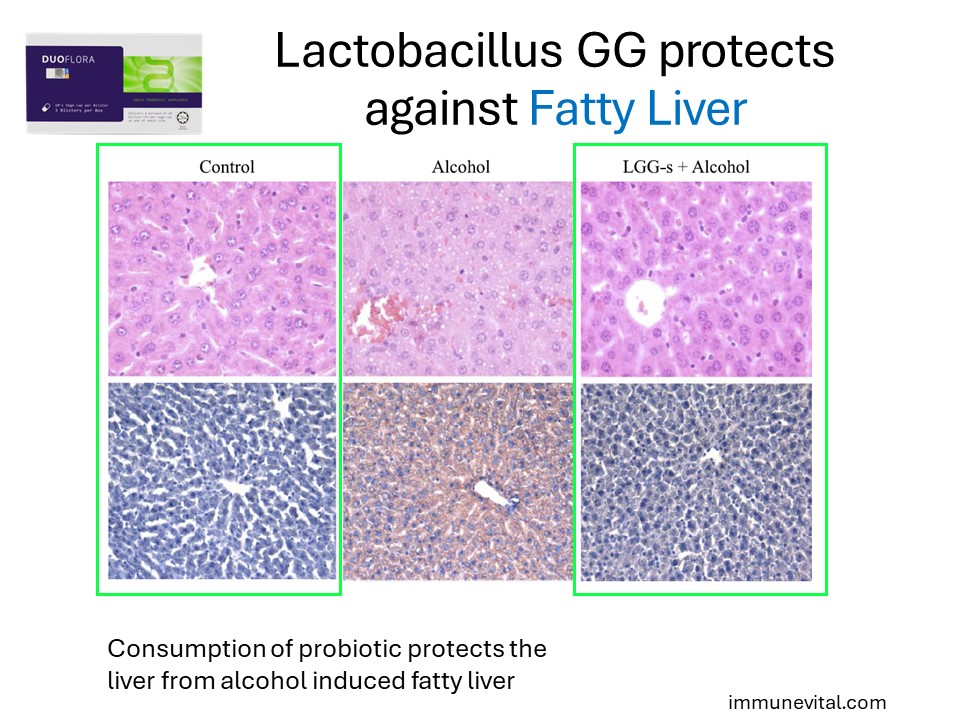
In the study above, supplementation with Lactobacillus GG was able to protect against alcohol induced liver damage and prevent development of fatty liver.
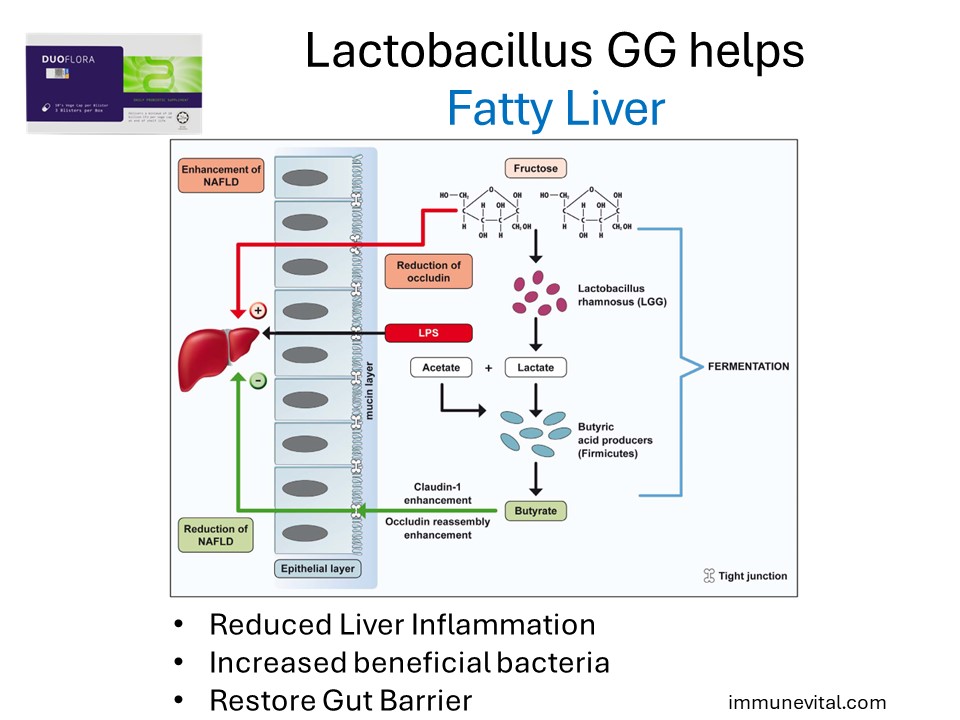
Lactobacillus GG protects from NAFLD induced by poor diet. The underlying mechanisms of protection likely involve an increase of beneficial bacteria, restoration of gut barrier function and subsequent attenuation of liver inflammation and steatosis.
Helps in Cancer
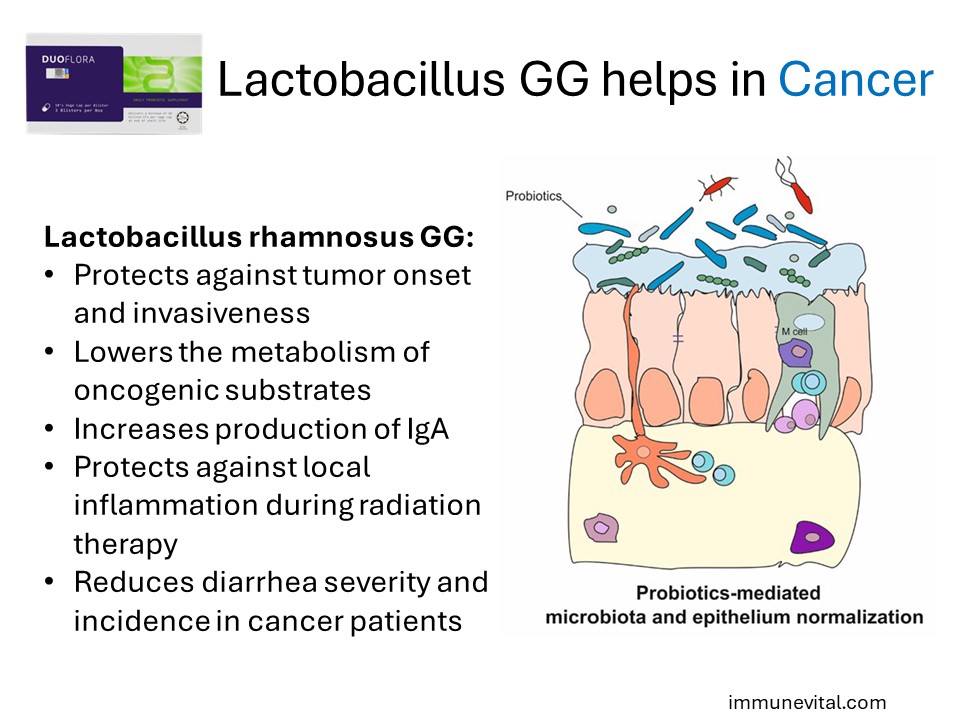
Lactobacillus GG’s role in cancer prevention and management is an exciting area of research. Some studies have indicated that Lactobacillus GG can inhibit the growth of certain cancer cells and enhance the immune response against tumors. Importantly, Lactobacillus GG can help during cancer treatments. It can reduce gastrointestinal inflammation and diarrhea in patients receiving chemo or radiation therapy. While more research is needed, the initial findings are promising and suggest a potential role for Lactobacillus GG in cancer therapy.
Conclusion
Lactobacillus GG is a multifaceted probiotic strain with a wide array of health benefits:
- Human strain probiotic that can colonize the human gastrointestinal tract
- Ability to reduce eczema severity
- Prevents eczema from developing in infants
- Helps food allergy to be outgrown
- Helps in Allergic Rhinitis and Asthma and reduces needs for medications
- Prevents and reduces duration of infectious diarrhea
- Helps in antibiotic associated diarrhea by reducing symptoms
- Reduces respiratory and gastrointestinal infections of children in the hospital or daycare
- Improves oral health and reduces tooth decay
- Helps relief symptoms of Irritable Bowel Syndrome and Abdominal Pain in both children and adults
- Protects liver from alcohol induced damage
- Prevents fatty liver from poor diet
- May help in patients with cancer undergoing chemo or radiation therapy
Science for your Health
References:
Isolauri E et al. Probiotics in the management of atopic eczema. Clin Exp Allergy 2000;30:1604-10
Canani RB et al. Effect of Lactobacillus GG on tolerance acquisition in infants with cow’s milk allergy- A randomized trial. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2012;129(2):580-582
Berni Canani R et al. Extensively hydrolyzed casein formula containing Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG reduces the occurrence of other allergic manifestations in children with cow’s milk allergy: 3-year randomized controlled trial. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2017 Jun;139(6):1906-1913.e4.
Kawase M et al. Effect of fermented milk prepared with two probiotic strains on Japanese cedar pollinosis in a double-blind placebo-controlled clinical study. Int J Food Microbiol 2009;128(3):429-434
Wu CT, Lin FH, Lee YT, Ku MS, Lue KH. Effect of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG immunopathologic changes in chronic mouse asthma model. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2019 Dec;52(6):911-919.
Kalliomäki M, Salminen S, Arvilommi H, Kero P, Koskinen P, Isolauri E. Probiotics in primary prevention of atopic disease: a randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 2001 Apr 7;357(9262):1076-9.
Kalliomäki M, Salminen S, Poussa T, Isolauri E. Probiotics during the first 7 years of life: a cumulative risk reduction of eczema in a randomized, placebo-controlled trial. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007 Apr;119(4):1019-21.
Guandalini S, Pensabene L, Zikri MA, et al: Lactobacillus GG administered in oral rehydration solution to children with acute diarrhea: a multicenter European trial. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr.2000 30(1):54–60.
Hilton E, Kolakowski P, Singer C, Smith M. Efficacy of lactobacillus GG as a diarrheal preventive in travelers. J Travel Med. 1997;4(1):41-43.
Vanderhoof JA, Whitney DB, Antonson DL, et al. Lactobacillus GG in the prevention of antibiotic-associated diarrhea in children.J Pediatr. 1999;135:564-568.
Armuzzi A, Cremonini F, Ojetti V, et al. Effect of lactobacillus GG supplementation on antibiotic-associated gastrointestinal side effects during helicobacter pylori eradication therapy: A pilot study. Digestion.2001;63(1):1-7.
Armuzzi A, Cremonini F, Bartolozzi F, et al. The effect of oral administration of lactobacillus GG on antibiotic-associated gastrointestinal side-effects during helicobacter pylori eradication therapy. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2001;15(2):163-169.
Cremonini F, Di Caro S, Covino M, et al. Effect of different probiotic preparations on anti-helicobacter pylori therapy-related side effects: A parallel group, triple blind, placebo-controlled study. Am J Gastroenterol. 2002;97(11):2744-2749.
Hojsak I, Snovak N, Abdović S, Szajewska H, Misak Z, Kolacek S. Lactobacillus GG in the prevention of gastrointestinal and respiratory tract infections in children who attend day care centers: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Clin Nutr. 2010 Jun;29(3):312-6.
Näse L, Hatakka K, Savilahti E, Saxelin M, Pönkä A, Poussa T, Korpela R, Meurman JH. Effect of long-term consumption of a probiotic bacterium, Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG, in milk on dental caries and caries risk in childrenn. Caries Res. 2001 Nov-Dec;35(6):412-20.
Kajander K et al. A Probiotic mixture alleviates symptoms in irritable bowel syndrome patients: a controlled 6-month intervention. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2005;22:387-394.
Francavilla R, Miniello V, Magistà AM, De Canio A, Bucci N, Gagliardi F, Lionetti E, Castellaneta S, Polimeno L, Peccarisi L, Indrio F, Cavallo L. A randomized controlled trial of Lactobacillus GG in children with functional abdominal pain. Pediatrics. 2010 Dec;126(6):e1445-52.
Forsyth CB et al. Lactobacillus GG treatment ameliorates alcohol-induced intestinal oxidative stress, gut leakiness, and liver injury in a rat model of alcoholic steatohepatitis. Alcohol 2009;43(2):163-172.
Wang Y et al. Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG culture supernatant ameliorates acute alcohol-induced intestinal permeability and liver injury. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 2012;303(1):G32-G41.
Ritze Y, Bárdos G, Claus A, Ehrmann V, Bergheim I, Schwiertz A, Bischoff SC. Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG protects against non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in mice. PLoS One. 2014 Jan 27;9(1):e80169.
Banna GL, Torino F, Marletta F, Santagati M, Salemi R, Cannarozzo E, Falzone L, Ferraù F and Libra M (2017) Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG: An Overview to Explore the Rationale of Its Use in Cancer. Front. Pharmacol. 8:603.